SRE Interview Questions
This page covers some different questions and categories an SRE might be expected to know
- SRE Interview Questions
- How and why would you use error budgets?
- Explain Blue-Green Deployment Technique
- What are some common deployment strategies?
- What is an SLA/SLI/SLO and how do they relate to each other
- What are the differences between continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment
- What is the difference between pull-based and push-based configuration management architecture
- Can you explain is impotency is or what it means when something is idempotent
- What is immutability
- Recommended Resources
- References
How and why would you use error budgets?
- An error budget is the amount of acceptable unreliability a service can have before customer happiness is impacted.
- If a service is well within its budget, the developers can take more risks in their releases.
- If not, developers need to make safer choices.
Explain Blue-Green Deployment Technique
- Blue-green deployment is a technique that reduces downtime and risk by running two identical production environments called Blue and Green. At any time, only one of the environments is live, with the live environment serving all production traffic. For this example, Blue is currently live and Green is idle.
- As you prepare a new version of your software, deployment and the final stage of testing takes place in the environment that is not live: in this example, Green. Once you have deployed and fully tested the software in Green, you switch the router so all incoming requests now go to Green instead of Blue. Green is now live, and Blue is idle.
- This technique can eliminate downtime due to application deployment. In addition, blue-green deployment reduces risk: if something unexpected happens with your new version on Green, you can immediately roll back to the last version by switching back to Blue.
What are some common deployment strategies?
Blue/Green
- Blue-green deployments are a pattern whereby we reduce downtime during production deployments by having two separate production environments ("blue" and "green").
Canary
- Canary deployments are a pattern for rolling out releases to a subset of users or servers.
- The idea is to first deploy the change to a small subset of servers, test it, and then roll the change out to the rest of the servers.
- The canary deployment serves as an early warning indicator with less impact on downtime: if the canary deployment fails, the rest of the servers aren't impacted.
Rolling
- Rolling deployments are a pattern whereby, instead of deploying a package to all servers at once, we slowly roll out the release by deploying it to each server one-by-one.
- In load balanced scenarios, this allows us to reduce overall downtime.
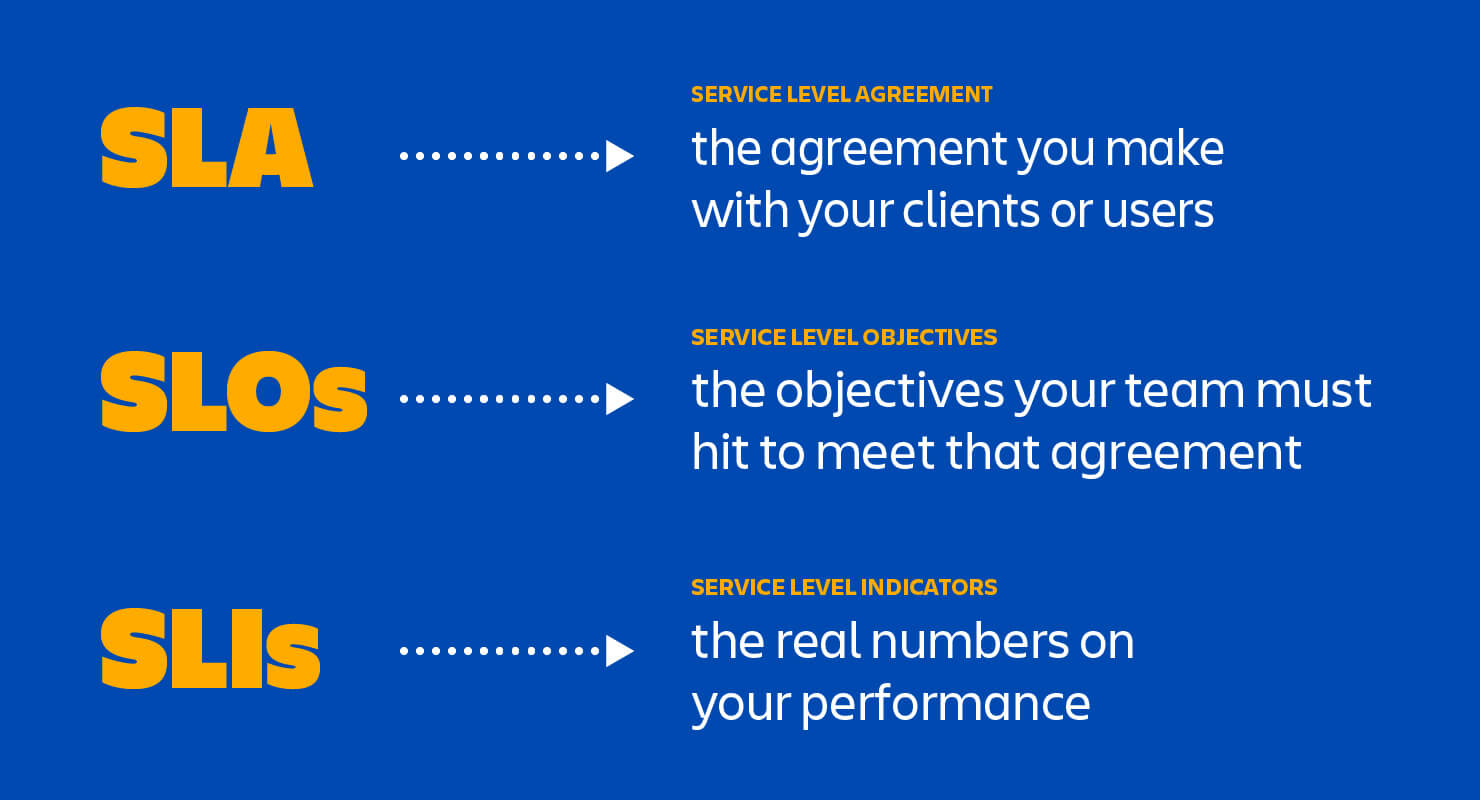
What is an SLA/SLI/SLO and how do they relate to each other
- An SLA (service level agreement) is an agreement between provider and client about measurable metrics like uptime, responsiveness, and responsibilities.
- An SLO (service level objective) is an agreement within an SLA about a specific metric like uptime or response time
- An SLI (service level indicator) measures compliance with an SLO (service level objective).
What are the differences between continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous deployment
- Developers practicing continuous integration merge their changes back to the main branch as often as possible. By doing so, you avoid the integration hell that usually happens when people wait for release day to merge their changes into the release branch.
- Continuous delivery is an extension of continuous integration to make sure that you can release new changes to your customers quickly in a sustainable way. This means that on top of having automated your testing, you also have automated your release process and you can deploy your application at any point of time by clicking on a button.
- Continuous deployment goes one step further than continuous delivery. With this practice, every change that passes all stages of your production pipeline is released to your customers. There's no human intervention, and only a failed test will prevent a new change to be deployed to production
What is the difference between pull-based and push-based configuration management architecture
- Pull Model: The nodes are dynamically updated by pulling the latest configuration from a centralized server.
- Push Model: Centralized server pushes the configurations to the nodes
Can you explain is impotency is or what it means when something is idempotent
-
The term impotency means that when changes are applied multiple times, the state is mutated (changed) just once. First, it already assumes that there are going to be changes applied which means that you cannot have something both immutable and have idempotent actions done to it (no actions are done to it by contract).
-
In the use of configuration management tools, impotency is used in some cases when applying the same change multiple times. Like adding the line that says localhost to the /etc/hosts file, you don't really need multiple such lines and if one already exists it is safe to not try to append again.
What is immutability
- Immutability, which literally means "no mutations" or "no changes". In the DevOps sense, it means that once you created an artifact, be that a container image, or a VM image, or maybe a package from compiled code - you declare that you will never ever change it. Often if any changes are required, you declare that a new version of "thing" will be created instead.
Recommended Resources
Courses
Articles
Books
- https://www.amazon.com/Practice-Cloud-System-Administration-Practices/dp/032194318X
- https://sre.google/books/
- https://www.amazon.com/Accelerate-Software-Performing-Technology-Organizations/dp/1942788339
- https://www.amazon.com/Phoenix-Project-DevOps-Helping-Business/dp/0988262592